Precious and semi-precious stones in the great majority are heated at high temperatures. Or subjected to radiation. That’s why ♦
If the precious stones warm your heart is perhaps because in turn have been heated. Not from your eyes, but from an electric furnace which can reach 1,600 degrees. The thermal treatment of precious and semiprecious stones is known to jewelers and gemologists, but little known to the general public, that is, those who buy jewelry that flaunt jewels of deep red, deep blue sapphires, aquamarines transparent. In fact, the colored stones that are sold as natural are a small minority, most end up in the oven, without the intervention of a chef. We see, then, what is the heat treatment of gemstones.

Warm color
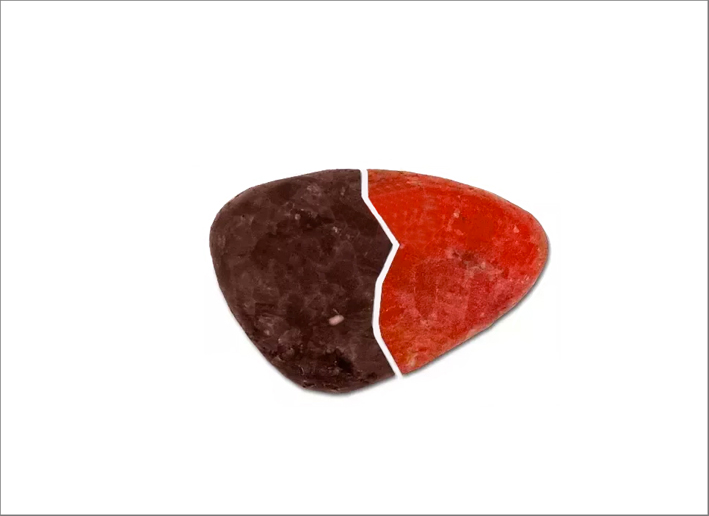
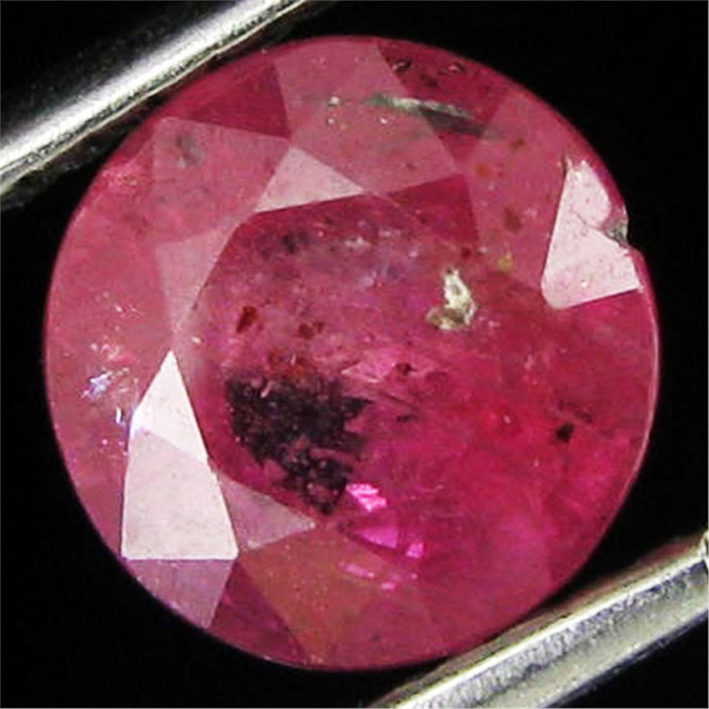
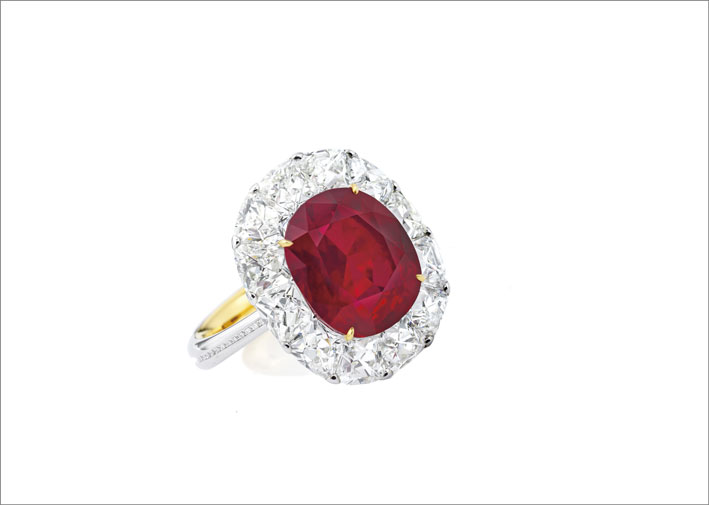
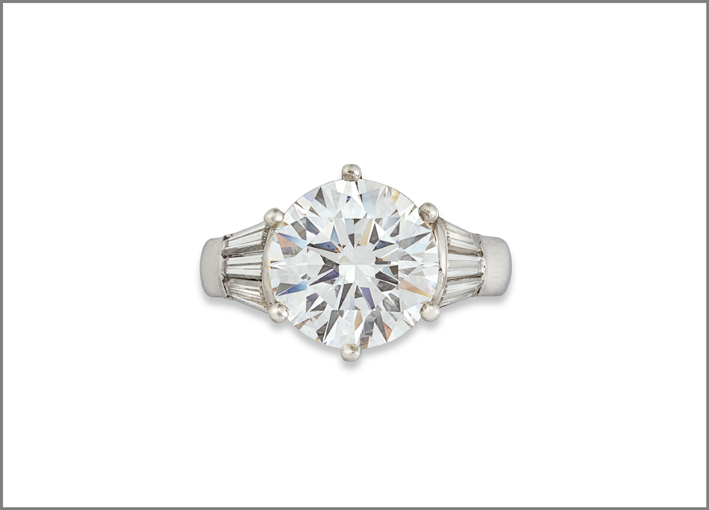
The stones are heated above all to bring out the colors. During treatment the stone is heated to very high temperatures (up to about 1600 degrees Celsius). At this temperature the inclusions (small amounts of other minerals) present in the stone melt and add their own color to the stone. Usually, therefore, the heated stone becomes darker, of a more intense hue. This is the case, for example, of rutile in the blue sapphires. There are also sapphires, known as Gouda, which are extracted from the ground milk and white sapphires turn blue when heated. Even the rubies are almost always heated (except exceptions): with the heat the aluminum oxide in the stone creates a new crystalline structure and the chromium is combined in a different way, allowing a better shade of red. Another effect of the heat is that it can improve the transparency of the stone, thanks to the destruction of any gas or fluid inclusions.

How to find them
Do you have a ring with a natural stone or heated? The question should be: what does it matter? But if you are curious to know, you must contact a gemologist with a microscope. And even so will not be easy to find out. The gemologists, however, can examine the internal state of the stone, inclusions, and look for signs of heat treatment. In general, if the stone is perfect or has exceptional value, or has been treated.
What stones are heated
Here the stones more easily end up in the oven: amethyst, citrine, ametrine, aquamarine, tourmaline, topaz, sapphire, ruby, tanzanite, blue zircon.
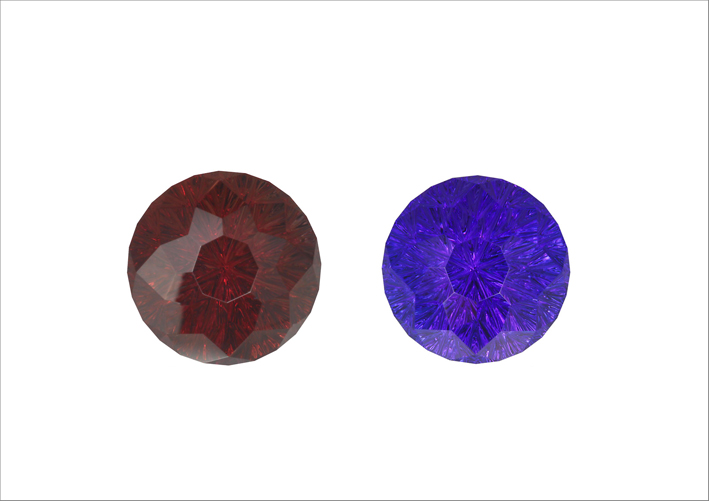
Irradiation
In addition to being heated, precious and semi-precious stones can be subjected to radiation. The question is: are they dangerous then? No, no problem: they are under strict control, just like when you go to the hospital for a chest screen. And, in any case, before leaving the laboratory the stones are checked to ensure that they do not emit dangerous radiation. After all, many gems are naturally subjected to radiation when underground. The irradiation that takes place in the laboratory serves to strengthen or change the color. A stone often subjected to radiation is blue topaz, which in nature is found with a very light shade. Often the two treatments, the thermal and the radioactive one, are combined: each one manages to improve a different aspect of the stone.














hello, do you know a heat treatment service provider for raw gemstones, such as ruby, particularly in canada?
Hi Mederic, unfortunately no, sorry